Beyond Conventional: Unlock Your Potential Through Neurodiversity-Affirming Therapy
Understanding Neurodiversity-Affirming Therapy for ADHD Women
TL;DR: Understanding Neurodiversity-Affirming Therapy for ADHD Women
- Neurodiversity-affirming therapy values and celebrates neurological differences, such as ADHD and autism, as natural variations, not deficits.
- Traditional therapy often tries to "normalize" behavior, which can be harmful and invalidating for a neurodiverse person
- This approach emphasizes self-acceptance, empowerment, and mental well-being by respecting each person's unique neurotype.
- It provides a supportive environment that is inclusive fosters personal growth and values differences.
- Key benefits for ADHD women include reduced internalized stigma, improved self-esteem, and a stronger sense of identity.
- The therapy can be combined with other approaches (like mindfulness or trauma-informed therapy) if adapted to respect neurodivergent needs.
Introduction
For many ADHD women, finding a supportive therapist can be challenging. Traditional therapy often focuses on "fixing" behaviors that are seen as different or "abnormal." Neurodiversity-affirming therapy, however, embraces these differences, recognizing them as natural variations in thinking and behavior.
This blog post will explore what neurodiversity is, describe neurodivergent-affirming therapy, and explain why it’s crucial for ADHD women and others with neurodevelopmental differences, such as autism, to understand their unique neurology.
Why is Neurodiversity-Affirming Therapy Important?
Traditional therapy approaches often aim to change or "normalize" behaviors, which can be harmful and invalidating for neurodivergent individuals. For ADHD women, finding therapists that validates their experiences and embraces their unique way of thinking is essential for fostering self-esteem, self-acceptance, and overall mental well-being.
Key Reasons for Neurodivergent-Affirming Therapy:
- Reduces internalized stigma by celebrating differences rather than viewing them as deficits.
- Supports mental health through self-acceptance and accommodations, and empowerment.
- Provides a safe, supportive environment that respects individuality and fosters growth.
What is Neurodiversity?
Neurodiversity is the concept that everyone’s brain works differently. It recognizes neurological differences as natural variations in human experience. This idea was introduced by Judy Singer, an autistic sociologist who argued that these differences should be accepted and celebrated rather than stigmatized. Conditions like ADHD, autism, dyslexia, and dyspraxia are viewed as unique neurotypes, much like different flowers in a garden—each bringing its unique beauty and value.
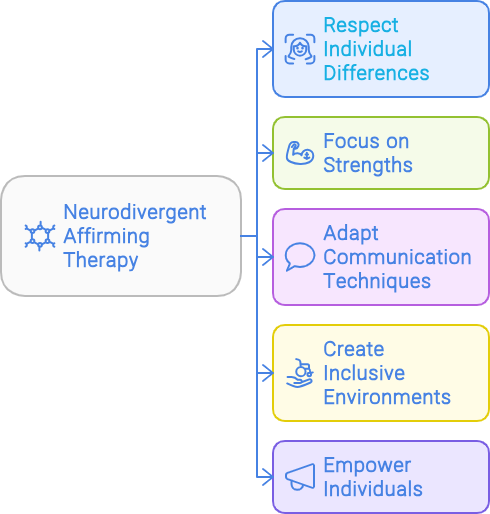
What is Neurodiversity-Affirming Therapy?
Neurodivergent-affirming therapy is a type of counseling that respects and values neurological differences. Unlike traditional therapies that often aim to "normalize" behavior, neurodivergent-affirming therapy focuses on understanding each person’s unique needs and strengths.
Core Principles
- Respect for Neurodiversity: Recognizes neurodivergent traits as natural variations, not deficits.
- Individualized Approach: Tailors therapy to each person’s unique strengths, brains, and challenges.
- Empowerment and Self-Advocacy: Encourages clients to understand their neurotype, advocate for themselves and understand their rights.
- Collaboration: Works with clients to develop personalized strategies that support their well-being.
- Safe and Supportive Environment: Provides a space that is free of judgment and accepting of all differences.

The Problem with Some Traditional Therapies
Some traditional therapies, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), have been problematic, particularly for neurodivergent individuals.
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): Often aims to change behaviors in people with autism spectrum disorder that are natural for neurodivergent people, such as "stimming" (self-soothing actions like flapping hands or rocking). These practices can be traumatic, as they force individuals to suppress behaviors that help them cope with sensory input or emotional stress. Many autistic adults have shared that these experiences were traumatic because they were compelled to act in ways that felt unnatural to them.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): While effective for some, CBT can feel overwhelming if not adapted to neurodivergent needs. It often focuses on changing thoughts and behaviors to fit neurotypical norms, which can make neurodivergent individuals feel misunderstood or pressured to conform. Many ADHD individuals have reported feeling confused or worse after such sessions, stating they felt "gaslit" and invalidated when their experiences were not acknowledged.

Why These Therapies Can Be Harmful:
- They may restrict natural behaviors or deny individuals the ability to express themselves in ways that are comfortable and natural.
- They often focus on changing behaviors to fit neurotypical standards, which can increase anxiety and depression and lower self-esteem.
- These approaches can lead to a sense of trauma, as individuals feel forced to mask or hide their true selves.
How Neurodiversity-Affirming Therapy Differs from Traditional Approaches
Neurodiversity-affirming therapy takes a different approach by focusing on understanding and celebrating differences rather than trying to eliminate them.
Key Differences:
- Embraces neurodivergent traits as strengths, not flaws.
- Encourages natural behaviors like stimming, recognizing them as valid coping mechanisms.
- Promotes self-determination and helps clients find ways to navigate a world that isn’t always accommodating.
FAQ: Neurodiversity-Affirming Therapy for ADHD Women
Q: What Techniques are Used in Neurodivergent-Affirming Therapy?
A: Providers with this expertise and knowledge use techniques and interventions like:
- Exploring Special Interests: Using passions as therapeutic tools to enhance engagement and motivation.
- Sensory Integration Strategies: Developing plans to manage sensory sensitivities and avoid overload.
- Communication Skills Development: Helping clients learn how to express their needs and boundaries.
- Emotional Regulation Strategies: Assisting clients in managing emotions in a way that respects their neurodivergent traits.
- Self-Advocacy Training: Teaching clients how to advocate for their needs in various settings.
- Adaptive Coping Mechanisms: Developing strategies that align with the client’s strengths and preferences.
- Masking Awareness and Reduction: Helping clients become aware of and reduce the pressures to "mask" or hide their neurodivergent traits, which can reduce anxiety and depression.
Q: How Can Neurodiversity-Affirming Therapy Help with Burnout?
A: It acknowledges that many neurodivergent individuals experience burnout from trying to fit into a neurotypical world. Therapy focuses on identifying specific stressors, such as sensory overload or social exhaustion, and developing strategies to manage these effectively. It also promotes self-care practices tailored to neurodivergent needs and encourages setting boundaries to protect mental and emotional well-being.
Q: Why is a Therapist's Understanding of Neurodivergence Crucial?
A: A therapist's understanding of neurodivergence ensures that therapy is genuinely supportive and affirming. A knowledgeable therapist avoids using harmful or invalidating techniques, such as discouraging stimming or pushing for eye contact. Instead, they provide interventions and guidance that respect the client’s neurodivergent identity, leading to more effective and meaningful outcomes.
Q: Can Neurodivergent-Affirming Therapy be Combined with Other Approaches?
A: Yes, it can be integrated with other therapies, such as mindfulness, narrative therapy, or trauma-informed therapy, provided these approaches are adapted to respect neurodivergent needs. The goal is to ensure that any integrated approach remains client-centered and affirming.
Conclusion
Neurodivergent-affirming therapy is about more than managing symptoms—it’s about celebrating differences and creating a supportive environment where neurodivergent individuals can thrive. If you’re seeking therapy, look for a therapist who understands neurodiversity, respects your needs, and is committed to helping you build on your strengths. Remember, your differences are not defects—they are what make you unique.
Resources
You can find some more info here at this listening of affirming therapists