🔍💡 Understanding ADHD: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Key Considerations for Women

ADHD: More Than Just Attention and Hyperactivity
"Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder" (ADHD) is a misleading name. ADHD isn't a disorder characterized by attention deficits or hyperactivity! On this page, we will explore what it is. We will also focus on the specific challenges ADHD women face, from diagnosis of symptoms to treatment.
From Misunderstood Behavior to Recognized Neurodivergence: Understanding the True Nature of ADHD
What Causes ADHD?
Understanding ADHD begins with recognizing its primary cause - genetics. ADHD is as genetic as height!
Although families can make ADHD children feel worse, parenting does not cause ADHD. Brain structures and neurotransmitter pathways are different in ADHD people, particularly in areas related to attention, reward systems, emotions, impulse control, and executive functions.
The neurotransmitter dopamine, crucial in attention and reward systems, is often disrupted. ADHD people have a dysregulation of dopamine. Genetic research has identified specific variations in genes such as DRD4 and DAT1.
ADHD Subtypes
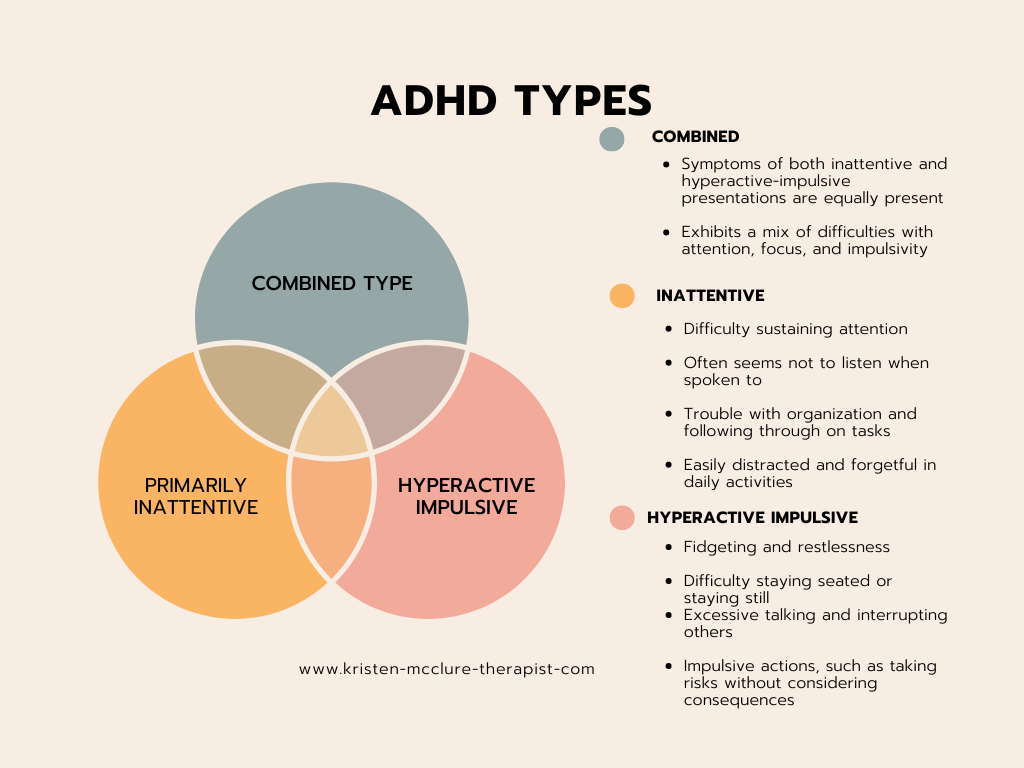
- The first type is Predominantly Inattentive Presentation. Girls and women are often diagnosed with inattentive ADHD. Inattentive ADHDers often struggle with maintaining attention, following detailed instructions, and organizing tasks. They might seem to listen but don't follow through on instructions. They usually get distracted easily.
Beyond Hyperactivity: Understanding ADHD as a Regulation Disorder
ADHD is about REGULATING and distributing attention. ADHD affects the ability to maintain and shift focus. An ADHD person might pay attention to the things they don't need to pay attention to. Individuals with ADHD have a remarkable knack for hyper-focusing on engaging tasks. However, they might struggle to redistribute their attention when necessary. Research shows that people with ADHD focus fine in the right environment. It must be one where they are interested and excited.

Hyperactivity in ADHD is often misunderstood, especially when it comes to girls and women.
In females, hyperactivity can manifest in less obvious ways:-
Internal Restlessness
-
Excessive Talking
-
Racing Minds
Executive Functioning Challenges
The Impact on Daily Functioning
ADHD significantly affects executive functioning, which includes skills like planning, motivation, remembering, and following through on tasks. Parents and teachers might mistakenly see children who struggle with these areas as defiant or disobedient. This misunderstanding can leave children feeling confused and bad about themselves.Misunderstandings in Adult Relationships
Adults with ADHD face similar misunderstandings in their relationships. They might forget to do things or fail to follow through, leading others to think they are lazy or don’t care. This can create stress at work, home, and social situations. These experiences often impact self-esteem, causing shame and confusion. This is particularly challenging for women, who are usually expected to use their executive functioning skills to juggle multiple roles effectively.Emotional Regulation Difficulties
The Challenges of Emotional Regulation Emotional regulation involves understanding your emotions and expressing them appropriately in different situations. However, if you struggle with emotional regulation, you might get easily overwhelmed, leading to difficulties in relationships and managing stress. As a result, this can affect your performance in school, social settings, and work. Furthermore, focusing and making decisions can be challenging when emotions feel overwhelming. Despite this, emotional regulation difficulties are often overlooked because they aren't part of the core ADHD criteria.Overlooked and Misdiagnosed in Girls
As a result, girls with ADHD are often overlooked or misdiagnosed. They may begin to hide their emotions, believing they are too much. Some might turn to substances or masking behaviors as a way to cope with their overwhelming feelings.Best Practices for Understanding ADHD Treatment
Effective treatment should consider the unique challenges of ADHD women.
Key Considerations and Skills:
-
🔆 Issues from trauma and grief from a late diagnosis
-
🔆 Addressing burnout
-
🔆 Affirming your nervous system's needs
-
🔆 Emphasizing self-compassion
-
🔆 Accommodating and learning about sensory differences
-
🔆 Prioritizing self-care to manage stress and prevent burnout
-
🔆 Learning self-advocacy skills, such as setting boundaries and communicating needs
-
🔆 Learning to self-accommodate
-
🔆 Managing energy and attention cycles
-
🔆 Understanding rejection sensitivity and learn how to feel safer
-
🔆 Supporting emotional regulation
-
🔆 Seeking assessment for other mental health issues like anxiety or depression
-
🔆 Finding support for alexithymia and interoception issues
-
🔆 Unmasking and reconnecting with your body
-
🔆 Developing practices to reduce anxiety and stress
-
🔆 Building a supportive network of peers and professionals
-
🔆 Exploring and embracing your unique strengths and interests
-
🔆 Supporting your executive functioning
-
🔆 Learning self-compassion to work on shame and self-criticism
-
🔆 Understanding and managing sensory overload
-
🔆 Setting realistic goals and celebrating small victories
-
🔆 Seeking education and resources on affirming neurodiversity to understand yourself better
-
🔆 Advocating for appropriate accommodations in work or school settings
-
🔆 Practicing positive interventions to support a happy brain
- 🔆 Support for physical issues from chronic stress, such as chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia and migraines





